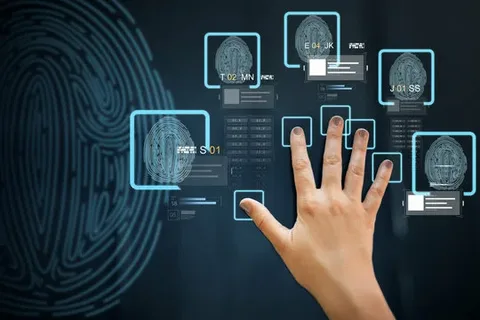
Biometric identity verification has emerged as a powerful tool for improving security and user convenience across industries. By using unique biological characteristics like fingerprints, facial features, and even voice, biometric identity verification offers a more secure and efficient way to verify an individual’s identity compared to traditional methods like passwords or PINs. In this article, we’ll explore what biometric identity verification is, how it works, its applications, and the latest trends in the field.
What is Biometric Identity Verification?
Biometric identity verification is a technology that uses physical or behavioral traits to identify and authenticate individuals. Unlike passwords, which can be forgotten or stolen, biometric traits are unique to each individual, making them a more reliable form of identity verification. Biometric systems capture an individual’s biometric data and compare it against a previously stored sample to confirm their identity.
Common biometrics used in identity verification include:
- Fingerprint recognition
- Facial recognition
- Iris and retinal scanning
- Voice recognition
- Palm vein recognition
How Does Biometric Identity Verification Work?
The biometric verification process generally follows these steps:
- Enrollment: During the initial setup, the system captures and stores a person’s biometric data, creating a digital template. This data is encrypted and securely stored for future comparisons.
- Data Capture: When verifying identity, the system captures a new biometric sample, such as a facial scan or fingerprint.
- Matching: The captured data is compared against the stored template using advanced algorithms to check for a match.
- Decision: If the data matches, the system grants access or verifies the transaction. If it does not match, the system denies access or flags the discrepancy for further investigation.
Types of Biometric Identification Technologies
- Fingerprint Recognition
- How it Works: Scans the unique patterns in a person’s fingerprints.
- Applications: Used extensively in smartphones, access control, and law enforcement.
- Pros and Cons: Fast and accurate but can be affected by skin conditions or injuries.
- Facial Recognition
- How it Works: Uses cameras to analyze facial features like the distance between eyes or the shape of the jaw.
- Applications: Popular in mobile devices, airports, and surveillance.
- Pros and Cons: Convenient and touchless; however, facial changes and lighting can affect accuracy.
- Iris and Retina Scanning
- How it Works: Uses specialized cameras to analyze unique patterns in the eye.
- Applications: High-security facilities and sensitive data access.
- Pros and Cons: Extremely accurate; however, requires specialized equipment and can be intrusive.
- Voice Recognition
- How it Works: Analyzes vocal patterns, tone, and pitch to identify individuals.
- Applications: Used in customer service, mobile banking, and virtual assistants.
- Pros and Cons: Convenient and effective for remote use; however, can be impacted by voice changes or background noise.
- Palm Vein Recognition
- How it Works: Scans the unique vein patterns in an individual’s palm.
- Applications: Often used in banking and healthcare.
- Pros and Cons: Highly accurate and difficult to spoof; requires contact or proximity to a scanner.
Advantages of Biometric Identity Verification
- Enhanced Security: Biometrics are difficult to fake or replicate, providing stronger security than traditional methods like passwords.
- User Convenience: Biometrics offer a seamless experience, allowing users to verify their identities quickly without needing to remember codes or carry identification.
- Reduced Fraud: By using unique biological characteristics, biometric systems help reduce identity fraud and unauthorized access.
- Scalability: Biometric systems can scale to verify large populations in real time, making them suitable for organizations with a high volume of users.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many industries are adopting biometrics to meet strict identity verification and fraud prevention regulations.
Applications of Biometric Identity Verification
Biometric identity verification is used in various industries to enhance security, reduce fraud, and streamline processes. Here are some key applications:
- Banking and Finance
- Banks use biometrics to provide secure login, prevent fraud, and offer KYC (Know Your Customer) services.
- Biometrics also enable secure online banking and payment authentication.
- Healthcare
- Biometrics help prevent identity fraud in medical records, protect patient data, and streamline access to healthcare services.
- Patient identities can be verified during hospital visits or while accessing digital health records.
- Travel and Border Control
- Facial recognition and fingerprinting are common at airports for identity verification and faster boarding.
- Biometrics improve border security by quickly identifying travelers and reducing wait times.
- Government and Law Enforcement
- Biometric data is used in passports, driver’s licenses, and national ID programs.
- Law enforcement agencies use biometrics for criminal identification and verification.
- Workplace Security
- Organizations use biometrics to control access to buildings or secure areas, ensuring only authorized personnel have access.
- Employee time tracking and attendance systems can also leverage biometrics.
Challenges of Biometric Identity Verification
- Privacy Concerns: Biometric data is highly sensitive, and users often worry about how their data is stored, used, and protected.
- Data Security: A breach involving biometric data can have serious implications since, unlike passwords, biometric data cannot be changed.
- Accuracy and Fairness: Environmental factors, physical changes, or differences in racial and ethnic groups can affect accuracy and lead to bias.
- Integration and Costs: Implementing biometric systems can be expensive and require infrastructure upgrades, especially for small businesses.
- Legal and Regulatory Issues: Data privacy laws, such as GDPR in Europe, impose strict requirements on biometric data usage, which can limit adoption.
Emerging Trends in Biometric Identity Verification
- Multimodal Biometrics: Combining multiple biometrics, such as fingerprint and face recognition, is gaining traction for improved accuracy and security.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI-powered biometric systems can analyze data more quickly and accurately, identifying complex patterns and adapting to changing biometric data.
- Mobile Biometrics: With the increasing use of smartphones, mobile biometrics are becoming popular for mobile banking, payments, and digital identity verification.
- Biometrics in E-Commerce: Online platforms are exploring biometrics for secure transactions and customer verification, enhancing the e-commerce shopping experience.
- Contactless Biometrics: Demand for touchless verification has risen post-pandemic, making face and voice recognition preferred options for secure and hygienic verification.
Future of Biometric Identity Verification
As biometric technology advances, it is expected to become even more accurate, affordable, and accessible. The integration of AI, machine learning, and IoT (Internet of Things) will likely make biometric verification more adaptive and resilient to fraud. Additionally, the convergence of biometrics with digital identities, blockchain, and cloud technology will open up new possibilities for secure, decentralized, and user-friendly identity verification solutions.
Conclusion
Biometric identity verification represents the future of secure and convenient identity authentication. While challenges remain, advancements in technology and regulatory measures are helping to address privacy and security concerns. As more industries adopt biometrics, we can expect a future where accessing secure services is as simple as scanning a fingerprint or looking into a camera. By embracing biometric solutions, businesses and governments can not only enhance security but also provide a smoother, faster, and more reliable experience for users around the world.